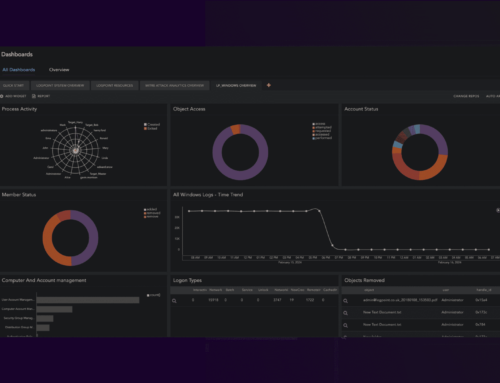
Data protection and cyber threat detection are crucial for businesses in today’s landscape. Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) plays a vital role in this regard. SIEM combines legacy tools like Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM) to offer cybersecurity professionals a centralized view of their IT infrastructure’s security. It collects and analyzes log data from various sources, providing real-time alerts, dashboards, and reports.
Some SIEM solutions integrate with technologies like Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) and User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) to automate threat response and detect abnormal behavior. Implementing a SIEM solution brings significant benefits. It allows real-time collection and analysis of data from all sources, including the growing volumes of data generated by organizations. Machine learning capabilities enhance threat detection, while the flexible and scalable architecture ensures adaptability to changing business needs. Improved investigation and incident response tools enable informed decision-making and swift response to threats. By reducing manual tasks and leveraging automation, SIEM solutions enhance the productivity of security analysts. Furthermore, some SIEMs offer predictable pricing models based on the number of nodes or the number of employees, freeing organizations from concerns about increasing data volumes. Delve deeper into the world of SIEM technology here:
Table of Contents
- 1 SIEM Definition – What is SIEM?
- 2 How Does SIEM Work?
- 3 What is a SIEM Tool Utilized For?
- 4 Limitations of Traditional SIEM Software
- 5 The Critical Role of SIEM
- 6 The Evolution of SIEM Technology
- 7 Benefits of a SIEM solution
- 8 How to Choose a SIEM Solution?
- 9 Businesses Collaborating with Logpoint for a SIEM Solution Can Expect:
- 10 Logpoint’s Value Proposition
SIEM Definition – What is SIEM?
SIEM stands for – Security Information & Event Management – and is a solution that combines legacy tools; SIM (Security Information Management) and SEM (Security Event Management). Some SIEM solutions also integrate with technology such as SOAR to automate threat response and UEBA to detect threats based on abnormal behavior. Together they provide accelerated detection and response to security events or incidents within an IT environment. It provides a comprehensive and centralized view of the security posture of an IT infrastructure and provides cybersecurity professionals with insights into the activities within their IT environment.
By collecting, storing, and analyzing log data from the entire IT infrastructure, SIEM performs real-time monitoring for threat detection, containment, and response before they harm organizations. SIEM solutions can also be used as a forensic tool to investigate past events for compliance or auditing purposes.
How Does SIEM Work?
SIEM software collects and aggregates log data generated throughout the entire IT infrastructure. This data can come from cloud systems and applications, endpoints, and network and security devices, such as firewalls and antivirus. SIEM then identifies, categorizes, and analyzes incidents and events. SIEM analytics delivers real-time alerts, dashboards, and reports to several critical business and management units. The log data collected enables automated response through SOAR and unsupervised machine learning for anomaly detection through UEBA.
What is a SIEM Tool Utilized For?
In the current landscape, data volume is increasing as are the number of cyber threats we face. So, companies should know that there’s no 100% security and they can be breached. A good SIEM solution helps security analysts to monitor and guard their data by raising alerts and reducing the MTTR (mean time to respond). With exploding data volumes and increasing complexity, as IT infrastructures converge towards hybrid deployments between cloud and on-prem, it is increasingly important to have a central security solution to track behavior and critical events.
However, the industry’s lack of skilled resources means that security events can overburden analysts and SOC teams, resulting in alert fatigue and confusion about prioritizing the company’s security resources.
Security Operation Centers (SOCs) thrive when there is less of a burden on them to perform – they need visibility. Without SIEM, security analysts must go through millions of disparate and siloed data for each application and security source. In short, SIEM can accelerate detection and response to cyber threats – making security analysts more efficient and accurate in their investigations.
SIEM software aids speed and accuracy in response to security incidents and provides centralized collection, classification, detection, correlation, and analysis capabilities. This makes it easier for teams to monitor and troubleshoot IT infrastructure in real-time.
Limitations of Traditional SIEM Software
SIEM tools have been around since 2005, but the SIEM definition and the answer to “What is SIEM?” have evolved. Changes in the threat landscape have created a need to identify a wider variety of threats quickly. For years, SIEM solutions were implemented to help security and IT teams analyze security alerts in real-time. Still, many traditional SIEM solutions cannot gather and analyze substantial amounts of data from various sources.
Due to the exponential growth of data volume, those who opt for SIEM solutions with a licensing model based on the number of logs ingested will face increasing costs and a lack of pricing predictability. So, many end up ingesting only security-specific logs to not exceed their budget. But this is a risky approach, as in the case of breaches, SOC teams are blind to abnormal behavior in their business-critical systems (BCS) and to other missing data, resulting in economic losses or regulatory fines.
At the same time, there is a shortage of security analysts available in the labor market. Security operations teams struggle to keep up with the deluge of security alerts from a growing arsenal of threat detection technologies while relying on rule-based manual procedures for operations. Fortunately, advanced analytics, investigation, and response tools combined with developments in machine learning, such as UEBA, create new efficiencies in SIEM solutions that help remedy the cybersecurity skills gap.
The Critical Role of SIEM
SIEM plays a crucial role in monitoring, detecting, and notification of security events or incidents within an IT environment. It provides a comprehensive and centralized view of the security posture of an IT infrastructure and provides cybersecurity professionals with insights into the activities within their IT environment.
The Evolution of SIEM Technology
In May 2005, Gartner put an end to the debate of what to choose, SIM or SEM, when they published their Improve IT Security with Vulnerability Management. They foresaw a combination of both technologies and coined the term SIEM, a solution that could manage raw logs and do it in real-time. Their recommendation was to consider broad-scope vendors for an integrated product that collected security data and analyzed it at the moment to detect patterns that lead to security issues.
And the story seemed to repeat itself when at the end of 2021 in one of their reports, Gartner predicted that platform consolidation would be the norm. According to them, “by 2025, 80% of enterprises will have adopted a strategy to unify web, cloud services and private application access from a single vendor’s security service edge (SSE) platform”.
The same rationale was applied to the creation of converged platforms that helped customers integrate their tech stack and minimize the number of security tools. Logpoint developed the idea of Converged SIEM.
Convergence
One of the outcomes of a converged platform is a faster TDIR process, as threat intel, operational context, and entity risk are automatically added to the alerts, and with orchestration and automation actions analysts can respond faster to threats. Logpoint Converged SIEM helps SOC teams combine data sets from multiple sources. Instead of using multiple standalone products, they now have one single source of truth. Converged SIEM is the only unified platform that delivers SIEM+SOAR, UEBA, EDR - endpoint security capabilities (Logpoint AgentX), and BCS for SAP capabilities as a service directly to enterprises and MSSPs – all from a single plane of glass.
It is an out-of-the-box platform, with no maintenance required. And as all different technologies are fully integrated into the platform, so is the data, resulting in reduced costs and more efficiency when operating at a larger scale.
In addition to this, a Converged SIEM platform should also help consolidation of other products too. Logpoint Converged SIEM offers support for more than 800 third-party integrations and applications. When platforms consolidate different tools, they immediately gain value that is greater than the sum of their parts.
Automate for Efficiency
Logpoint SOAR is an innovative security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solution that brings cybersecurity efficiency and effectiveness to businesses.
Pairing SIEM with SOAR combines security monitoring and incident response to help security staff quickly respond to and resolve incidents. A SOAR solution automates actions and responses, handling incidents that don’t need the security team’s attention. By doing so, it not only reduces the risk of human error but also the analyst’s workload.
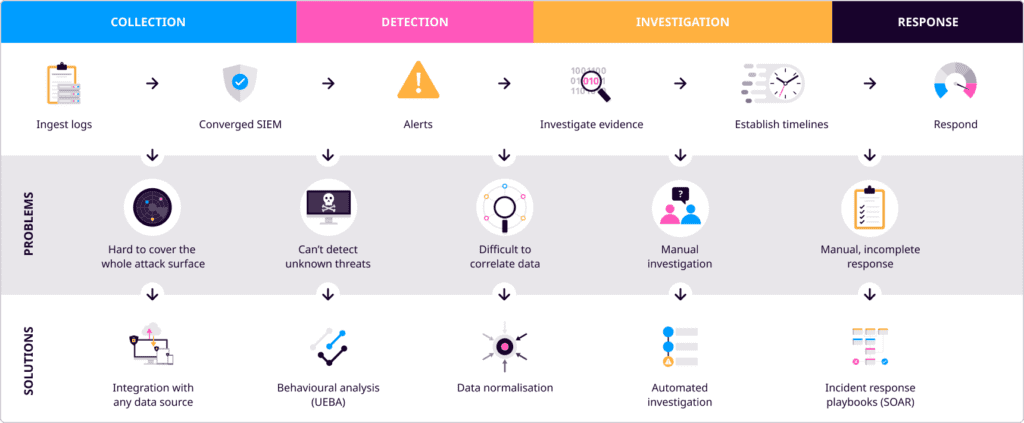
Benefits of a SIEM solution
To establish a capable cybersecurity team, SIEM is a must-have for businesses of any size and in any industry. Today’s enterprises need a solution to centralize, simplify, and automate security workflows to enable better analytics and incident response procedures.
The Seven Key Benefits of SIEM technology are:
1. Real-time collection and analysis of data from all sources
Organizations are generating more data than ever before. To keep up with the increase of data, SIEM tools must ingest data from all sources, including cloud and on-premises, to effectively monitor, detect, and respond to potential threats.
The more data an organization can provide its SIEM software, the more visibility analysts will have into the activities, and the more effective they will be in detecting and responding to threats. These logs and telemetry will enrich both the SIEM and the SOAR events for better response and easier compliance checks.
2. It utilizes machine learning to add context and situational awareness to increase efficiency
Today’s attacks are becoming more sophisticated, meaning organizations need equally sophisticated tools. Attackers often rely on compromised credentials or the coercion of users into performing actions that damage their organization. To identify these threats quicker, SIEM tools should be equipped with machine learning capabilities that enable the monitoring of suspicious user behavior from internal and external threats like UEBA.
With UEBA, organizations will see a dramatic increase in their SIEM’s ability to track and identify threats. UEBA limits false positives, so analysts have better situational awareness before, during, and after a threat – increasing efficiency and enabling spending their limited time on real threats.
3. Its flexible and scalable architecture improves time to value
The amount of data produced by organizations has grown exponentially over the past few years, resulting in organizations needing big data architectures that are flexible and scalable and can adapt and grow as the business changes over time. A SIEM can deploy in virtual environments, on-premises, or in the cloud with the ability to handle complex implementations. Some provide a short implementation time and minimal maintenance resource requirements, resulting in the SIEM value developing within days.
4. It provides enhanced investigation and incident response tools
SIEMs go beyond essential security monitoring and reporting. They provide analysts with the clarity they need to improve decision-making and response time, innovative data visualization, and intelligent business context to help better interpret and respond to the instruction of the data. The incident response becomes more sophisticated, and better analytics means teams can efficiently manage incidents and improve their forensic investigations within a single interface.
5. It makes security analysts more productive from day 1
Once logs are collected, a SIEM system must provide use cases to help the security team detect and respond to threats immediately. For example, correlation rules, compliance standards, and detecting insider threats are all readily available use cases the SIEM provides across all applications immediately from implementation.
6. It reduces cybersecurity staff requirements
Today’s security teams are time-constrained, so enhanced automation frees analysts from manual tasks. It enables them to orchestrate responses to threats better. The best SIEMs utilize machine learning to help ease the burden of overworked security analysts. This is done by automating threat detection, providing enhanced context and situational awareness (such as threat intelligence), and utilizing user behavior to gain better insights.
7. It comes with predictable pricing
SIEM licensing models based on data usage are outdated. Data volumes are continually increasing, and organizations shouldn’t be punished for that. SIEM pricing models should instead be based on the number of devices sending logs, meaning organizations don’t have to worry about the impact on cost, allowing them to focus on scaling.
Make sure you analyze the total cost of ownership and also when the SIEM security needs to scale. Some vendors have added costs when increasing hardware capabilities, integrating with other tools, and ingesting logs from other applications.
How to Choose a SIEM Solution?
When choosing a SIEM solution, businesses should consider organizing a workshop internally or with a SIEM partner to define and agree on the project scope and timeline. To determine the organization’s scope and timeline, you must identify and, more importantly, prioritize an initial list of use cases to dictate what the necessary log sources may be. It is also essential to agree upon a timeline for deployment to ensure the SIEM security aligns with the business goals.
The four key questions to consider in the process of choosing a SIEM solution are;
- WHAT applications to focus on?
- HOW to respond when threats are detected?
- WHERE are the most critical threats to your environment?
- WHY are these the most critical threats, and what is the impact of a breach?
Planning a SIEM project: The three main steps
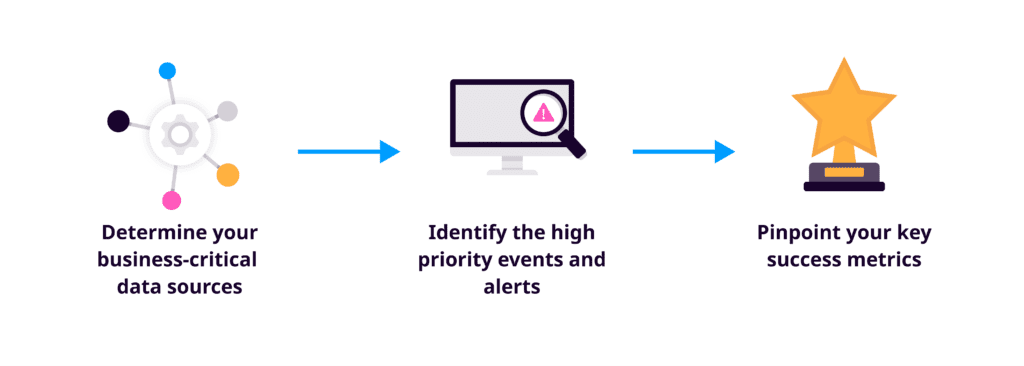
Determine your business-critical data sources
Once you have a handle on the ideal project scope, you can then identify log sources within the scope to determine how to obtain the relevant data needed. For example, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software serve as prime data sources for SIEM security use cases. But there are many more, including routers, web filters, domain controllers, application servers, databases, and other digitally connected assets. You must prioritize the sources included to ensure the SIEM provides the desired data to support the selected use cases.
Identify the high-priority events and alerts
When it comes to protecting an organization against insider and external threats, security teams face an ever-growing list of security events that need to be analyzed and acted upon. To break through the noise, SIEM software can be used to make events and data more insightful. Still, businesses must first determine their high-priority events and how to derive them from applications and devices within the infrastructure. This way, security teams can use the SIEM to spend more time on incidents and alerts that may be critical to the business and its data.
Pinpoint your key success metrics
A successful SIEM implementation aligns with your business goals. Key success metrics must be determined before deployment to ensure maximum ROI. For example, reducing data theft or improving how businesses detect potential breaches or insider threats may be metrics to establish. But there are many others. Companies must determine what success means for them and how SIEM security use cases can be used to achieve it.
Businesses Collaborating with Logpoint for a SIEM Solution Can Expect:
Better threat detection and response
A SIEM solution provides real-time data analysis, early detection of data breaches, data collection, secure data storage, and accurate data reporting to improve threat detection and response times.
Fewer staff
The automation of functions frees security analysts from time-consuming manual tasks and enables them to better orchestrate a response to threats. The best SIEM solutions utilize machine learning and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to help ease the burden of overworked security analysts.
Less spend
A SIEM solution with a simple and predictable licensing model enables businesses to spend less to keep their data secure, regardless of the amount of data they have and the number of sources from which data is logged.
Logpoint’s Value Proposition
We have a history of success in IT security and in safeguarding businesses from risk and mitigating reputational and financial damage. By providing a simplified overview of your IT infrastructure you can make impactful business decisions.
By using, our advanced UEBA technology solution, based on machine learning, we give your security team an edge. We ensure less business downtime by enabling your team to respond and detect threats faster and more efficiently.
The SIEM solution integrates easily with all devices in your network, giving a holistic and correlated overview of events in your IT infrastructure.
Logpoint’s SIEM solution translates all data into one common language, making it possible to compare events across all systems. This common language makes it very easy and efficient to search, analyze and report on the data. This helps accelerates the team’s detection and response rate to threats reducing workload.
For compliance initiatives, Logpoint enables automatic monitoring of relevant compliance parameters and alerts you to relevant risks as they happen. Our SIEM solution is easy to use with a low learning curve for busy professionals. We also drive operational efficiencies by supporting a proactive approach to understanding your network, and by providing actionable, real-time insight into your IT infrastructure to drive business value.