AgentTesla [S0331] a.k.a Negasteal is a .NET-based Remote Administrator Tool (RAT) first detected in 2014. It is advertised as a Remote Administrator Tool since then. AgentTesla allows adversaries to remotely control the systems of victims and manipulate them accordingly, so it is utilized by numerous threat actors such as SILVERTERRIER, SWEED, Aggah, etc.
Initially, it only had remote administrator capabilities but after various iterations and upgrades, recent variations are capable of spying on victim systems, capturing sensitive data such as credentials, and users’ actions by recording screen and keylogging, stealing credentials from browsers and mail clients, and exfiltrate those collected data using various techniques. The interesting part is, it has the capability to extract data from a large number of browsers and mail clients and utilizes various protocols to exfiltrate those data. The malware utilizes various obfuscation techniques such as software packing [T1027.002], and encoded payloads [T1027] to evade defense.
It has been spreading rapidly in the wild with CISA listing it in the Top Malware Strains list for the year 2021 and it still is in the top 10 list on MalwareBazaar as of March 2023.
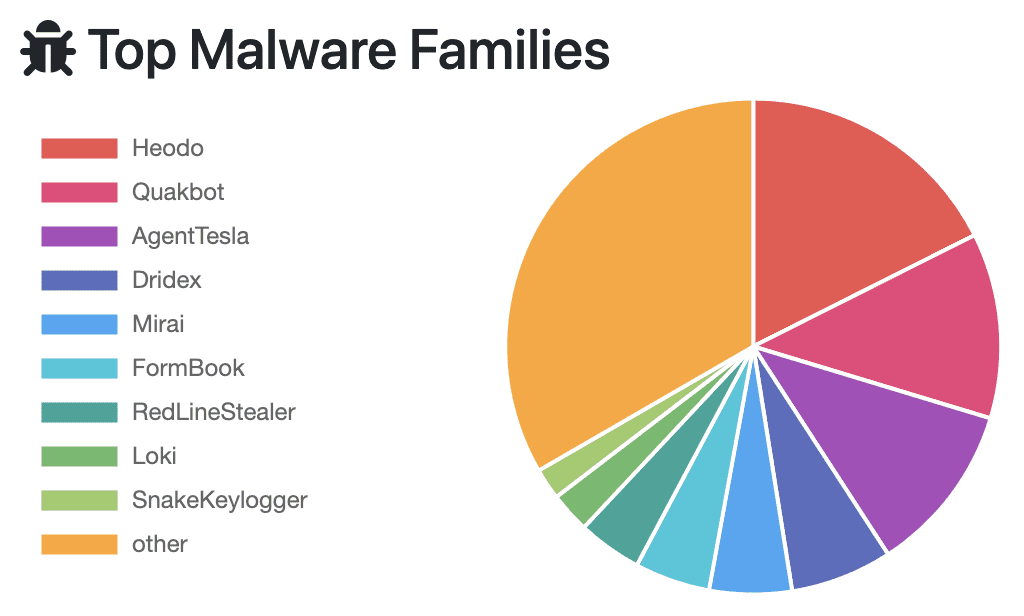
Source - MalwareBazaar
The operators of AgentTesla are providing Malware-as-a-Service with various pricing options for different versions of the malware. During the year 2017, the malware’s website was available on the public internet (now on the dark web), and advertising about the RAT capabilities with various price ranges and features.
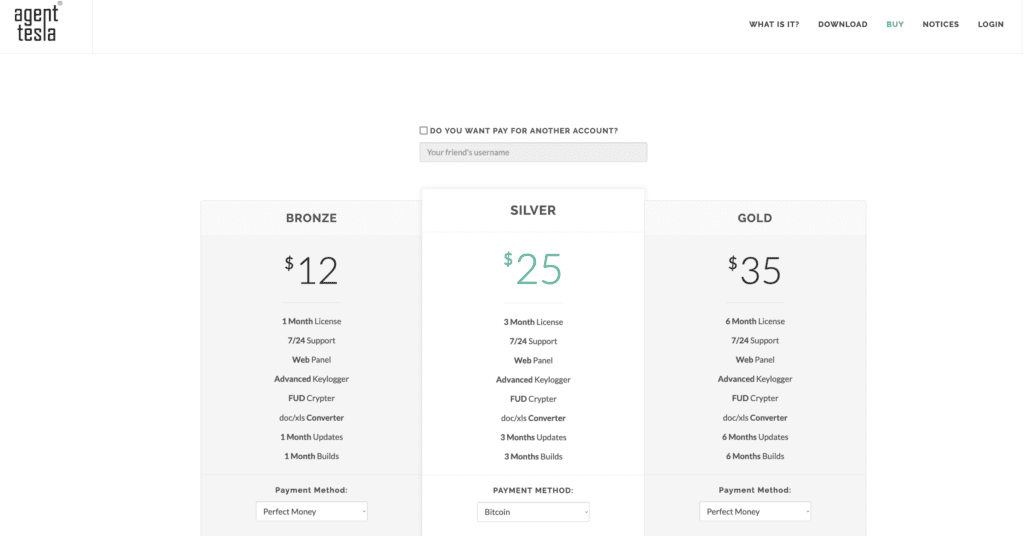
AgentTesla Marketing Site, 2017 Source - WebArchieve
The price shown above has likely been changed. It is provided for reference purposes purely to show that AgentTesla provides multiple buying options and operates a business-like model. AgentTesla has been used in numerous campaigns by multiple threat actors as it is available to be bought at various price ranges with various capabilities and support from the operators. In 2022, CERT-UA discovered AgentTesla being deployed in their state organization systems through phishing attachments [T1566.001]. Besides Ukraine, the AgentTesla malware was also seen being deployed in a data theft campaign by threat actors tracked as Aggah against East European countries.
Infection Chain
It all starts with phishing attachments, whereby victims are lured to execute malicious attachments. It can range from LNK files to Office documents with malicious macros or payload to exploit vulnerabilities such as CVE-2017-0199 (Remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Office Application and WordPad) and CVE-2017-11882 (Remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft office).
Once the initial payload is executed, it tries to connect to the malware distribution site and download other stages of payload, and finally downloads AgentTesla into the system. The initial payload can also directly download the malware without dropping other payloads. After AgentTesla is in the system, various actions are performed such as persistence, credential harvesting, and exfiltration.
For persistence techniques the malware schedules tasks [T1053] or places itself in startup folders or under registry Run keys [T1547.001]. In the case of data collection, what we have observed is that it has a predefined list of browsers, mail, and VPN client. Based on whichever mentioned services and application is present in the system, it tries to retrieve data from them. For exfiltration, we found various samples of AgentTesla utilizing various protocols and applications such as SMTP, FTP, Telegram, and Discord.
We go into full detail on how the malware is being distributed, and the infection chain and provide an analysis of its capabilities in the attached report. We uncover some of the TTPs from the analysis of malware and case studies. After understanding its capabilities we have provided detection rules to detect the malware at various stages through its known behavior which is available to download as part of Logpoint’s latest release, as well as through Logpoint’s download center (https://servicedesk.logpoint.com/hc/en-us/articles/115003928409).
Logpoint Emerging Threats Protection Service provides the service subscribers with customized investigation and response playbooks, tailored to your environment. Contact the global services team here.
The report contains the analysis, detection, and mitigation using Logpoint SIEM+SOAR can be downloaded from the link.








